Ở bài viết trước, tôi đã hướng dẫn bạn cách cài đặt danh sách liên kết đơn và các kiến thức về danh sách liên kết. Bài viết này, mình sẽ hướng dẫn bạn cài đặt danh sách liên kết đôi nhé. Danh sách liên kết đôi có sự liên kết 2 chiều giữa 2 phần tử liền kề nhau trong khi danh sách liên kết đơn chỉ có liên kết 1 chiều.
1. Lý thuyết về Danh sách liên kết đôi
Một Node của danh sách liên kết đôi sẽ có dạng như sau:
---------------------------------------------
| | | |
| PREV | DATA | NEXT |
| | | |
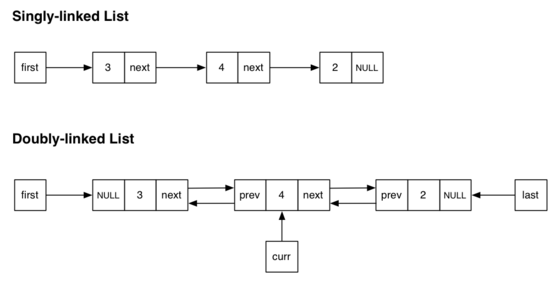
---------------------------------------------Và hình dưới đây so sanh sự khác nhau giữ dslk đôi và dslk đơn:
2. Cài đặt danh sách liên kết đôi
2.1. Khai báo & khởi tạo
Khác một chút với dslk đơn, ngoài con trỏ next, chúng ta sẽ có thêm con trỏ prev để liên kết với Node trước nó. Chúng ta vẫn sẽ để data có kiểu int để đơn giản và dễ hiểu nhé.
Ngay sau khai báo, chúng ta sẽ khởi tạo Node đầu tiên của danh sách liên kết đôi.
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
struct Node* head; // Khởi tạo Node head global của dslk đôi.2.2. Tạo mới 1 Node
Thay vì chỉ cho next = NULL và gán giá trị cho Node mới, chúng ta cũng phải cho con trỏ prev = NULL.
struct Node* GetNewNode(int x) {
struct Node* newNode
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = x;
newNode->prev = NULL;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}2.3. Thêm Node
Thêm vào đầu
- Nếu head = NULL, ta sẽ cho cả head và tail = newNode.
- Nếu head != NULL, ta sẽ cập nhật lại head mới là newNode. Ta cần tạo liên kết giữa head hiện tại với newNode trước khi cho newNode làm head mới.
void InsertAtHead(int x) {
struct Node* newNode = GetNewNode(x);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
return;
}
head->prev = newNode;
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
}Về cơ bản, ý tưởng thêm Node vào đầu/ cuối vẫn giống với thêm vào đầu trong danh sách liên kết đơn.
Thêm vào cuối
- Nếu head = NULL, newNode sẽ là head và tail luôn
- Nếu head != NULL, cập nhật lại tail mới là newNode. Ta cần tạo liên kết thằng tail hiện tại với newNode trước khi để newNode làm tail mới.
void InsertAtTail(int x) {
struct Node* newNode = GetNewNode(x);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
return;
}
tail->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = tail;
tail = newNode;
}2.4. Xóa Node
Xóa ở đầu
- Nếu head = NULL, chẳng có gì để xóa
- Nếu head != NULL, cho head mới bằng phần tử tiếp theo và sửa prev của nó = NULL(ngắt liên kết với thằng head cũ).
void DeleteAtHead() {
if(head == NULL) {
return;
}
head = head->next;
head->prev = NULL;
}Xóa ở cuối
- Nếu head = NULL, chẳng có gì để xóa
- Nếu head != NULL, cho tail mới bằng phần tử trước nó và sửa next của nó = NULL(ngắt liên kết với thằng tail cũ).
void DeleteAtTail() {
if(head == NULL) {
return;
}
tail = tail->prev;
tail->next = NULL;
}2.5. Duyệt danh sách liên kết
Duyệt từ đầu tới cuối
Ta sẽ duyệt bắt đầu từ Node head cho tới trước khi gặp Node NULL bằng cách dùng con trỏ next.
void Print() {
struct Node* temp = head;
printf("nForward: ");
while(temp != NULL) {
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("n");
}Duyệt từ cuối về đầu
Lần này, ta sẽ duyệt bắt đầu từ Node tailcho tới trước khi gặp Node NULL bằng cách dùng con trỏ prev.
void ReversePrint() {
struct Node* temp = tail;
if(temp == NULL) return; // empty list, exit
// Traversing backward using prev pointer
printf("nReverse: ");
while(temp != NULL) {
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp = temp->prev;
}
printf("n");
}3. Full code danh sách liên kết đôi
/* Doubly Linked List implementation */
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
struct Node *head, *tail; // Khởi tạo Node head global của dslk đôi.
//Creates a new Node and returns pointer to it.
struct Node* GetNewNode(int x) {
struct Node* newNode
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = x;
newNode->prev = NULL;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
//Inserts a Node at head of doubly linked list
void InsertAtHead(int x) {
struct Node* newNode = GetNewNode(x);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
return;
}
head->prev = newNode;
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
}
//Inserts a Node at tail of Doubly linked list
void InsertAtTail(int x) {
struct Node* newNode = GetNewNode(x);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
return;
}
tail->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = tail;
tail = newNode;
}
void DeleteAtHead() {
if(head == NULL) {
return;
}
head = head->next;
head->prev = NULL;
}
//Inserts a Node at tail of Doubly linked list
void DeleteAtTail() {
if(head == NULL) {
return;
}
tail = tail->prev;
tail->next = NULL;
}
//Prints all the elements in linked list in forward traversal order
void Print() {
struct Node* temp = head;
printf("nForward: ");
while(temp != NULL) {
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("n");
}
//Prints all elements in linked list in reverse traversal order.
void ReversePrint() {
struct Node* temp = tail;
if(temp == NULL) return; // empty list, exit
// Traversing backward using prev pointer
printf("nReverse: ");
while(temp != NULL) {
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp = temp->prev;
}
printf("n");
}
int main() {
/*Driver code to test the implementation*/
head = NULL; // empty list. set head as NULL.
// Calling an Insert and printing list both in forward as well as reverse direction.
InsertAtTail(2);
Print(); ReversePrint();
InsertAtTail(4);
Print(); ReversePrint();
InsertAtHead(6);
Print(); ReversePrint();
InsertAtTail(8);
Print(); ReversePrint();
DeleteAtHead();
Print(); ReversePrint();
DeleteAtTail();
Print(); ReversePrint();
}
Kết quả chạy:
Forward: 2 Reverse: 2 Forward: 2 4 Reverse: 4 2 Forward: 6 2 4 Reverse: 4 2 6 Forward: 6 2 4 8 Reverse: 8 4 2 6 Forward: 2 4 8 Reverse: 8 4 2 Forward: 2 4 Reverse: 4 2 Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.040 s Press any key to continue.


Để lại một bình luận