[Hướng dẫn Prolog] Prolog là ngôn ngữ được sử dụng phổ biến trong lĩnh vực trí tuệ nhân tạo. Nguyên lý lập trình logic dựa trên các mệnh đề Horn (Horn logíc). Bài viết này Nguyễn Văn Hiếu Blog sẽ hướng dẫn bạn cách sử dụng ngôn ngữ Prolog: Cú pháp Prolog, biến & các kiểu dữ liệu của Prolog, cách xây dựng sự kiện và luật trong Prolog đi kèm ví dụ.
1. Một số thuật ngữ về Prolog
Một chương trình Prolog là một cơ sở dữ liệu gồm các mệnh đề (clause). Mỗi mệnh đề được xây dựng từ các vị từ (predicat). Một vị từ là một phát biểu nào đó về các đối tượng có giá trị chân đúng (true) hoặc sai (fail). Một vị từ có thể có các đối là các nguyên lôgich (logic atom).
Mỗi nguyên tử (nói gọn) biểu diễn một quan hệ giữa các hạng (term). Như vậy, hạng và quan hệ giữa các hạng tạo thành mệnh đề.
Hạng được xem là những đối tượng “dữ liệu” trong một trình Prolog. Hạng có thể là hạng sơ cấp (elementary term) gồm hằng (constant), biến (variable) và các hạng phức hợp (compound term).
Các hạng phức hợp biểu diễn các đối tượng phức tạp của bài toán cần giải quyết thuộc lĩnh vực đang xét. Hạng phức hợp là một hàm tử (functor) có chứa các đối (argument), có dạng:
Tên_hàm(tham số 1, tham số 2,..., tham số n)
Tên hàm là một chuỗi chữ cái và/hoặc chũ số được bắt đầu bởi một chữ cái thường. Các đối có thể là biến, hạng sơ cấp, hoặc hạng phức hợp.
Ví dụ:
- f(5, a, b).
- student(robert, 1975, info, 2,
- address(6, ‘mal juin’, ‘Caen’)).
- [a, b, c]
Mệnh đề có thể là một sự kiện, một luật (hay quy tắc), hay một câu hỏi. Prolog quy ước viết sau mỗi mệnh đề một dấu chấm để kết thúc như sau :
- Sự kiện : < … >. (tương ứng với luật < … > :- true. )
- Luật : < … > :- < … >.
- Câu hỏi ?- < … >. (ở chế độ tương tác có dấu nhắc lệnh)
2. Xây dựng luật
Ví dụ về luật:
woman(mary). man(tom). man(bill). woman(liz). woman(sue). woman(ann). man(jim).
Ta đã định nghĩa các quan hệ đơn (unary) woman và man vì chúng chỉ liên quan đến một đối tượng duy nhất. Còn quan hệ parent là nhị phân, vì liên quan đến một cặp đối tượng. Như vậy, các quan hệ đơn dùng để thiết lập một thuộc tính của một đối tượng. Mệnh đề :
woman(mary).
được giải thích : Mary là nữ. Tuy nhiên, ta cũng có thể sử dụng quan hệ nhị phân để định nghĩa giới tính:
sex(mary, female). sex(tom, male).
Bây giờ ta đưa vào một quan hệ mới child, đối ngược với parent như sau:
child(liz, tom).
Từ đó, ta định nghĩa luật mới như sau:
child(Y, X) :- parent(X, Y).
Luật trên được hiểu là: Với mọi X và Y, Y là con của X nếu X là cha (hay mẹ) của Y.
Hoặc: Với mọi X và Y, nếu X là cha (hay mẹ) của Y thì Y là con của X.
3. Ví dụ chương trình tư vấn ngôn ngữ lập trình
Dưới đây là chương trình Prolog tư vẫn ngôn ngữ lập trình. Các bạn copy về và lưu thành một file có đuôi là “.pl”. Sau đó dùng Prolog để chạy theo hướng dẫn phía dưới. Các bạn có thể tham khảo chương trình sau để hiểu hơn về ngôn ngữ Prolog.
Chú ý: Nếu bạn chưa cài Prolog, hãy đọc bài viết Cách kết nối Prolog với C# trên Visual Studio. Trong bài này sẽ có hướng dẫn bạn cách cài Prolog và có chương trình Hệ chuyên gia tư vấn chọn ngôn ngữ lập trình sử dụng Winform C#.
% Author:
% Date: 11/29/2017
% Expert system should be started from here
go :-
intro,
reset_answers,
find_language(Language),
describe(Language), nl.
intro :-
write('Which programming language should I learn first?'), nl,
write('To answer, input the number shown next to each answer, followed by a dot (.)'), nl, nl.
find_language(Language) :-
language(Language), !.
% Store user answers to be able to track his progress
:- dynamic(progress/2).
% Clear stored user progress
% reset_answers must always return true; because retract can return either true
% or false, we fail the first and succeed with the second.
reset_answers :-
retract(progress(_, _)),
fail.
reset_answers.
% Rules for the knowledge base
language(python) :-
why(for_my_kids).
language(python) :-
why(i_dont_know).
language(java) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(doesn_t_matter).
language(cpp) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(gaming).
language(objectivec) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(mobile),
which_mobile_os(ios).
language(java) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(mobile),
which_mobile_os(android).
language(python) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(facebook).
language(python) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(google).
language(csharp) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(microsoft).
language(objectivec) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(apple).
language(javascript) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(web),
web(front_end).
language(csharp) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(web),
web(back_end),
want_to_work_for(corporate),
think_about_microsoft(im_a_fan).
language(java) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(web),
web(back_end),
want_to_work_for(corporate),
think_about_microsoft(not_bad).
language(java) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(web),
web(back_end),
want_to_work_for(corporate),
think_about_microsoft(suck).
language(javascript) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(web),
web(back_end),
want_to_work_for(startup),
try_something_new(yes).
language(python) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(web),
web(back_end),
want_to_work_for(startup),
try_something_new(no),
favourite_toy(lego).
language(ruby) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(web),
web(back_end),
want_to_work_for(startup),
try_something_new(no),
favourite_toy(play_doh).
language(php) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(web),
web(back_end),
want_to_work_for(startup),
try_something_new(no),
favourite_toy(old_ugly).
language(csharp) :-
why(make_money),
which_platform(enterprise),
think_about_microsoft(im_a_fan).
language(java) :-
why(make_money),
want_to_work_for(enterprise),
think_about_microsoft(not_bad).
language(java) :-
why(make_money),
want_to_work_for(enterprise),
think_about_microsoft(suck).
language(python) :-
why(just_for_fun),
prefer_to_learn(easy_way).
language(python) :-
why(just_for_fun),
prefer_to_learn(best_way).
language(java) :-
why(just_for_fun),
prefer_to_learn(harder_way),
car(auto).
language(c) :-
why(just_for_fun),
prefer_to_learn(harder_way),
car(manual).
language(cpp) :-
why(just_for_fun),
prefer_to_learn(hardest_way).
language(python) :-
why(im_interested),
prefer_to_learn(easy_way).
language(python) :-
why(im_interested),
prefer_to_learn(best_way).
language(java) :-
why(im_interested),
prefer_to_learn(harder_way),
car(auto).
language(c) :-
why(im_interested),
prefer_to_learn(harder_way),
car(manual).
language(cpp) :-
why(im_interested),
prefer_to_learn(hardest_way).
language(python) :-
why(improve_myself),
prefer_to_learn(easy_way).
language(python) :-
why(improve_myself),
prefer_to_learn(best_way).
language(java) :-
why(improve_myself),
prefer_to_learn(harder_way),
car(auto).
language(c) :-
why(improve_myself),
prefer_to_learn(harder_way),
car(manual).
language(cpp) :-
why(improve_myself),
prefer_to_learn(hardest_way).
% Questions for the knowledge base
question(why) :-
write('Why do you want to learn programming?'), nl.
question(which_platform) :-
write('Which platform/field?'), nl.
question(which_mobile_os) :-
write('Which OS?'), nl.
question(web) :-
write('Which "end"?'), nl.
question(want_to_work_for) :-
write('I want to work for...'), nl.
question(think_about_microsoft) :-
write('What do you think about Microsoft?'), nl.
question(try_something_new) :-
write('Do you want to try something new, with huge potential, but less mature?'), nl.
question(favourite_toy) :-
write('Which one is your favourite toy?'), nl.
question(prefer_to_learn) :-
write('I prefer to learn things...'), nl.
question(car) :-
write('Auto or Manual car?'), nl.
% Answers for the knowledge base
answer(for_my_kids) :-
write('For my kids').
answer(i_dont_know) :-
write('I don't know').
answer(make_money) :-
write('Make money').
answer(just_for_fun) :-
write('Just for fun').
answer(im_interested) :-
write('I'm interested').
answer(improve_myself) :-
write('Improve myself').
answer(doesn_t_matter) :-
write('Doesn't matter, I just want $$$').
answer(gaming) :-
write('3D/Gaming').
answer(mobile) :-
write('Mobile').
answer(facebook) :-
write('Facebook').
answer(google) :-
write('Google').
answer(microsoft) :-
write('Microsoft').
answer(apple) :-
write('Apple').
answer(web) :-
write('Web').
answer(enterprise) :-
write('Enterprise').
answer(ios) :-
write('iOS').
answer(android) :-
write('Android').
answer(front_end) :-
write('Front-end (web interface)').
answer(back_end) :-
write('Back-end ("brain" behind a website)').
answer(startup) :-
write('Startup').
answer(corporate) :-
write('Corporate').
answer(im_a_fan) :-
write('I'm a fan!').
answer(not_bad) :-
write('Not Bad').
answer(suck) :-
write('Suck').
answer(yes) :-
write('Yes').
answer(no) :-
write('No').
answer(lego) :-
write('Lego').
answer(play_doh) :-
write('Play-Doh').
answer(old_ugly) :-
write('I've an old & ugly toy, but I love it so much!').
answer(easy_way) :-
write('The easy way').
answer(best_way) :-
write('The best way').
answer(harder_way) :-
write('The slightly harder way').
answer(hardest_way) :-
write('The really hard way (but easier to pick up other languages in the future)').
answer(auto) :-
write('Auto').
answer(manual) :-
write('Manual').
% Language descriptions for the knowledge base
describe(python) :-
write('Python'), nl,
write('Widely regarded as the best programming language for beginners'), nl,
write('Easiest to learn').
describe(java) :-
write('Java'), nl,
write('One of the most in demand & highest paying programming languages'), nl,
write('Slogan: write once, work everywhere').
describe(c) :-
write('C'), nl,
write('Lingua franca of programming language'), nl,
write('One of the oldest and most widely used language in the world').
describe(cpp) :-
write('C++'), nl,
write('Complex version of C with a lot more features'), nl,
write('Recommended only if you have a mentor to guide you').
describe(javascript) :-
write('JavaScript'), nl,
write('Most popular clients-side web scripting language'), nl,
write('A must learn for front-end web developer (HTML and CSS as well)').
describe(csharp) :-
write('C#'), nl,
write('A popular choice for enterprise to create websites and Windows application using .NET framework'), nl,
write('Similar to Java in basic syntax and some features').
describe(ruby) :-
write('Ruby'), nl,
write('Mostly known for its popular web framework, Ruby on Rails'), nl,
write('Focuses on getting things done').
describe(php) :-
write('PHP'), nl,
write('Suitable for building small and simple sites within a short time frame'), nl,
write('Supported by almost every web hosting services with lower price').
describe(objectivec) :-
write('Objective-C'), nl,
write('Primary language used by Apple for MacOSX & iOS'), nl,
write('Choose this if you want to focus on developing iOS or OSX apps only').
% Assigns an answer to questions from the knowledge base
why(Answer) :-
progress(why, Answer).
why(Answer) :-
+ progress(why, _),
ask(why, Answer, [for_my_kids, i_dont_know, make_money, just_for_fun, im_interested, improve_myself]).
which_platform(Answer) :-
progress(which_platform, Answer).
which_platform(Answer) :-
+ progress(which_platform, _),
ask(which_platform, Answer, [doesn_t_matter, gaming, mobile, facebook, google, microsoft, apple, web, enterprise]).
which_mobile_os(Answer) :-
progress(which_mobile_os, Answer).
which_mobile_os(Answer) :-
+ progress(which_mobile_os, _),
ask(which_mobile_os, Answer, [ios, android]).
web(Answer) :-
progress(web, Answer).
web(Answer) :-
+ progress(web, _),
ask(web, Answer, [front_end, back_end]).
want_to_work_for(Answer) :-
progress(want_to_work_for, Answer).
want_to_work_for(Answer) :-
+ progress(want_to_work_for, _),
ask(want_to_work_for, Answer, [startup, corporate]).
think_about_microsoft(Answer) :-
progress(think_about_microsoft, Answer).
think_about_microsoft(Answer) :-
+ progress(think_about_microsoft, _),
ask(think_about_microsoft, Answer, [im_a_fan, not_bad, suck]).
try_something_new(Answer) :-
progress(try_something_new, Answer).
try_something_new(Answer) :-
+ progress(try_something_new, _),
ask(try_something_new, Answer, [yes, no]).
favourite_toy(Answer) :-
progress(favourite_toy, Answer).
favourite_toy(Answer) :-
+ progress(favourite_toy, _),
ask(favourite_toy, Answer, [lego, play_doh, old_ugly]).
prefer_to_learn(Answer) :-
progress(prefer_to_learn, Answer).
prefer_to_learn(Answer) :-
+ progress(prefer_to_learn, _),
ask(prefer_to_learn, Answer, [easy_way, best_way, harder_way, hardest_way]).
car(Answer) :-
progress(car, Answer).
car(Answer) :-
+ progress(car, _),
ask(car, Answer, [auto, manual]).
% Outputs a nicely formatted list of answers
% [First|Rest] is the Choices list, Index is the index of First in Choices
answers([], _).
answers([First|Rest], Index) :-
write(Index), write(' '), answer(First), nl,
NextIndex is Index + 1,
answers(Rest, NextIndex).
% Parses an Index and returns a Response representing the "Indexth" element in
% Choices (the [First|Rest] list)
parse(0, [First|_], First).
parse(Index, [First|Rest], Response) :-
Index > 0,
NextIndex is Index - 1,
parse(NextIndex, Rest, Response).
% Asks the Question to the user and saves the Answer
ask(Question, Answer, Choices) :-
question(Question),
answers(Choices, 0),
read(Index),
parse(Index, Choices, Response),
asserta(progress(Question, Response)),
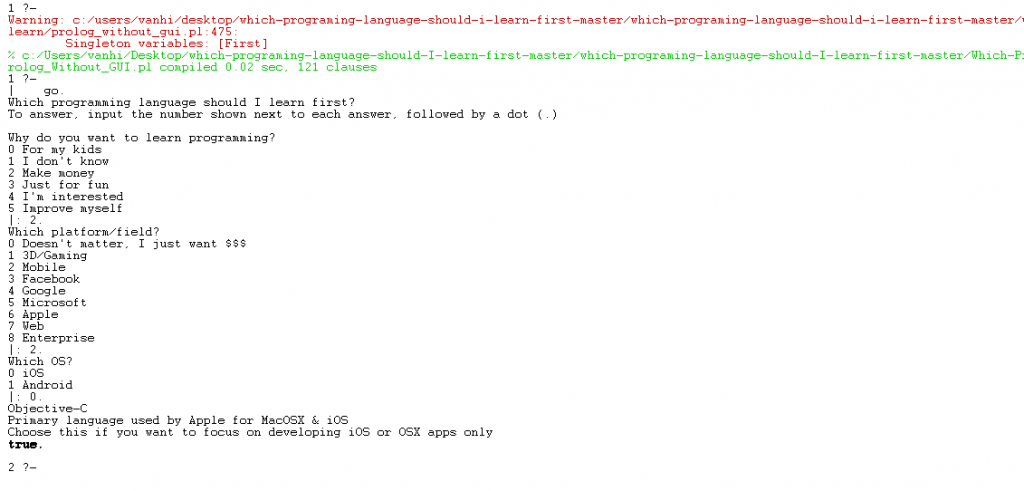
Response = Answer.Để chạy file Prolog này. Bạn làm theo trình tự sau:
- Mở Prolog lên, vào menu
File -> Consult, sau đó chọn đến file Prolog này. - Sau khi Consult xong. Gõ
go.để chạy thử chương trình



Để lại một bình luận